Application - Types
Table of Content:
Application - Types
Applications are broadly classified into two types:
i) Monolithic Architecture, where an application is built as a single unit.
ii) Microservices Architecture, where many applications (microservices) handle a small portion of the functionality and data.
We will discuss both these types in detail.
Fact# 3
According to Gartner Hype Cycle for Application Services, 2016, Microservices is rated at the peak.
Monolithic Style
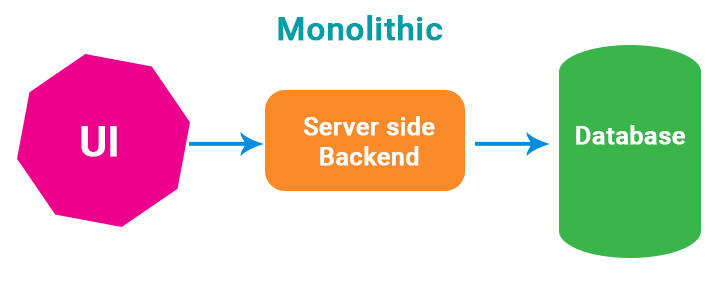
-
A monolithic application is built as a
single unit, i.e., one big application in a single language that handles all of thefunctionality, data, business logicetc. A load balancer distributes requests from the end user, across multiple machines, each running one instance of our application. -
All logic for handling a request runs in a single process, allowing you to utilize the primary features of the language to divide up the application into
classes, functions, and namespaces.
Monolithic Style - Advantages
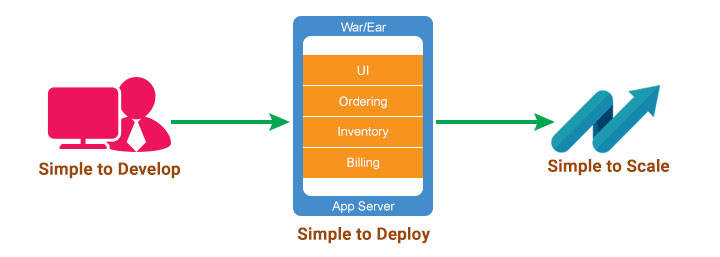
- Faster Initial Development - With one application, it would be relatively easy to add additional features, especially when the application is relatively small.
- Little User Confusion - Developers need not have to learn about different applications, but would be focused towards one application.
- Improved Integration - Features could integrate with each other well and easily.
Monolithic Style - Disadvantages
-
Single Point of Failure- If any single applicationfunctionorcomponentfails, then the entire application goes down. For example - a web application with separate functions handling tasks like payment, login, and history; a function begins to consume more memory or CPU. In this scenario, the entire application will come to a halt. -
Horizontal Scaling- Scaling application can only be accomplished by deploying the same EAR/WAR packages in more servers. Every single copy of the application in different servers will use the same number of primary resources, which is usually not an effective way to design.
- As
application grows, the code base grows with it, which can overload IDE every time it loads the application. This definitely reduces developer productivity. - Substantially
less iteration- a small change made to any part of the application, requires the entire monolith to be rebuilt and deployed. Maintenance costswill shoot up exponentially with site size.High set-up costs- In order to get each new volunteer up and running, the larger the application, the more difficult this would be.
Fact# 4
Cypherpath predicted that in 2017 onwards more vendors will specialize in supporting the deployment of microservices as a business model.
Microservice Style
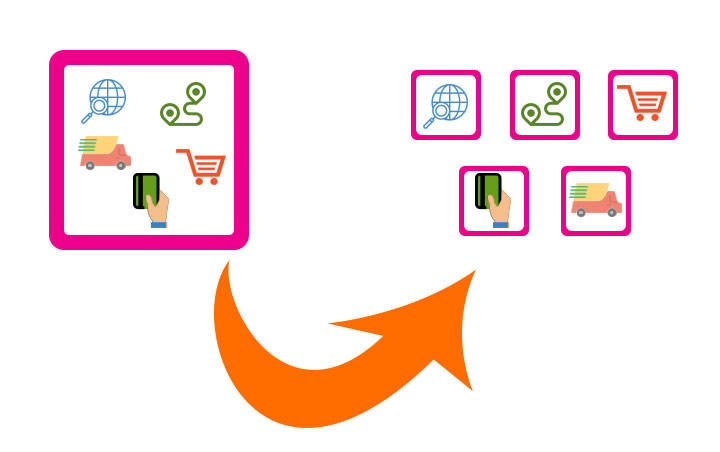
Build applications as suites of services (Modular approach)
-
Each microservice exposes a common API accessed through the network (as opposed to inter-process communication or shared memory on the same machine).
-
API calls are stitched mostly on the server to produce a page, although few of this work is executed by the client querying individual microservices.
Big enterprise players such as Amazon, Netflix, Uber, Yelp and eBay have adopted Microservices. Services are
- Independently deployable
- Scalable
Each service offers a secure module boundary, allowing different services to be written in different programming languages.
Microservice Style - Advantages
- Improved fault isolation: Larger applications can remain largely unaffected by the failure of a single module with microservice style adoption.
- Removes Dependency: Eliminates long-term commitment to any single technology stack.
- Easy Understanding: With the split of functionality, it gives more room for new developers to understand the functionality of a service and make enhancements easily.
- Easy Deployment: Microservices-based applications are deployed inside containers providing better management.
Microservice Style - Disadvantages
- Complexity - Deploying microservices can be a little complex, requiring coordination among multiple services, which may not be as straightforward as deploying a monolith.
- Multiple DBs - Managing multiple databases and transaction management could be painful.
- Testing - Testing could be little cumbersome, as each dependent service needs to be confirmed before one can start testing.
- Coordination - Handling requests across multiple independent services requires proper workflow management. There can be a scenario where one of the services may not be responding or remote calls experiencing latency.
