Three Constructs That Govern Statement Flow
Table of Content:
⚙️ Three Constructs That Govern Statement Flow
Every Java program (and almost all programming languages) is built using three fundamental control structures:
🔹 1. Sequence
Definition:
The sequence construct means that statements are executed one after another in the same order in which they appear in the program.
Example:
|
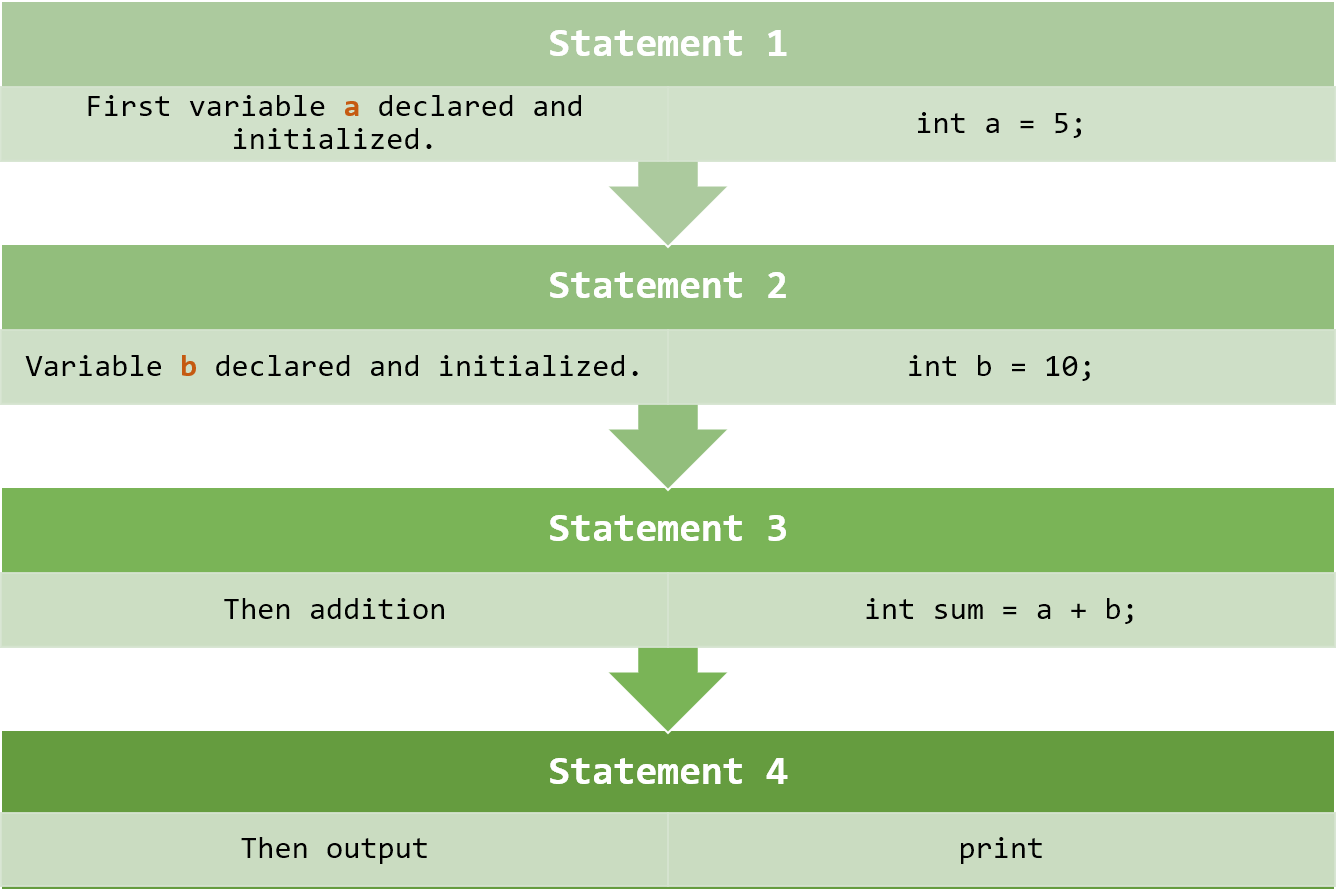 |
Explanation:
Here, each line executes sequentially —
first variables are declared → then addition → then output.
No skipping or repetition of statements.
🔹 2. Selection (Decision Making)
Definition:
The selection construct allows the program to choose a path of execution based on a condition.
It uses if, if-else, or switch statements.
Example:
public class SelectionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 10;
if (number % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("Even number");
} else {
System.out.println("Odd number");
}
}
}
Explanation:
Here, the program selects one path depending on whether the condition number % 2 == 0 is true or false.
🔹 3. Iteration (Looping)
Definition:
The iteration construct allows statements to be executed repeatedly as long as a condition is true.
It uses loops such as for, while, or do-while.
Example:
public class IterationExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Count: " + i);
}
}
}
Explanation:
The statement inside the loop executes five times, controlling the flow through repetition.
🧠 Summary Table
| Construct | Purpose | Keyword/Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence | Executes statements in order | — | Simple statements |
| Selection | Chooses one path based on condition | if, if-else, switch |
Decision making |
| Iteration | Repeats a set of statements | for, while, do-while |
Looping |
